How Latency Affects Website Speed
11/14/2025 • 14 min read

How Latency Affects Website Speed
Latency kills website speed and user satisfaction. It’s the delay in transferring data between a user’s device and your server, and even milliseconds matter. A 100ms delay can drop conversion rates by 7%, while 53% of mobile users abandon pages that take over 3 seconds to load.
Here’s what you need to know:
- Latency vs. Bandwidth: Latency measures delay, while bandwidth measures data capacity. High bandwidth doesn’t fix slow responses caused by latency.
- Business Impact: Amazon loses 1% of sales for every 100ms of delay. Walmart saw a 2% conversion boost by speeding up page loads by 1 second.
- Causes: Long distances, network congestion, server inefficiencies, and bloated code all contribute.
- Solutions: Use CDNs, optimize code, compress images, and implement caching for faster load times.
Speed isn’t just about user experience - it drives revenue, boosts search rankings, and builds trust. Fixing latency is a must for any website aiming to stay competitive.
How to improve website performance and optimize page speed
How Latency Impacts User Experience and Business Results
Latency isn't just a technical hiccup - it can ruin user experiences and take a serious toll on your business's bottom line. When users encounter delays, their engagement drops, and revenue suffers. That’s why tackling latency issues should be a priority for any online business.
User Experience Problems from High Latency
High latency creates a frustrating experience for users. When pages are slow to load or buttons lag, users abandon tasks. Google’s research shows that as page load time increases from 1 second to 10 seconds, the likelihood of a mobile user bouncing jumps by 123%. That’s a staggering figure.
Slow-loading websites also harm trust. People start to see your brand as unreliable, which can discourage them from sharing sensitive information or returning in the future. Mobile users, who often deal with slower networks, are even more likely to leave a site that doesn’t load quickly.
Engagement metrics also take a hit. Visitors to slow websites spend less time on them, view fewer pages, and interact less with forms, buttons, and other interactive elements. This drop in engagement can hurt your search engine rankings, as search engines factor user behavior into their algorithms.
Akamai’s research found that 53% of mobile site visits are abandoned if pages take longer than 3 seconds to load. Beyond the frustration this causes users, these issues lead to measurable business losses.
Business Impact of Latency
The user experience problems caused by latency directly translate into financial losses. For example, Amazon reported that every 100-millisecond increase in latency costs them 1% in sales. To put that into perspective, a company earning $100,000 a day could lose $2.5 million in annual sales from just a one-second delay.
Conversion rates are particularly sensitive to latency. Akamai’s study revealed that a 100-millisecond delay in load time can reduce conversion rates by 7%. Fixing latency issues, therefore, can be one of the most effective ways to boost your website’s performance and revenue.
Real-world examples highlight this even further. Back in 2012, Walmart found that every 1-second improvement in page load time increased conversions by 2%. Similarly, Mozilla shaved 2.2 seconds off their Firefox download page load time in 2011, resulting in a 15.4% increase in downloads.
Even more recent examples back up these findings. Avery G., Growth Lead at ShopHive, reported a 24% increase in trial conversions after fixing bottlenecks in their website’s user flow. Another product manager noted a 32% boost in completed checkouts after optimizing slow-loading pages that had been deterring shoppers.
Latency also affects search engine optimization (SEO). Search engines prioritize fast-loading pages in their rankings, so a slow website could mean fewer organic visitors. And fewer visitors mean fewer conversions and less revenue.
The long-term effects on your brand are just as damaging. Users frustrated by slow websites are less likely to return or recommend your business. Negative word-of-mouth can linger, even after performance issues are resolved. On top of that, high latency increases customer acquisition costs by lowering conversion efficiency, making paid advertising less effective and reducing the return on marketing investments.
What Causes Latency in Website Performance
To tackle latency effectively, it’s important to understand where it comes from. Latency can arise from various sources, including network infrastructure, server performance, and client-side challenges. Each of these factors contributes to delays in how users interact with a website. Let’s break down the main causes.
Network-Related Factors
Physical distance is a major culprit behind network latency. Even in our hyper-connected world, data takes time to travel. For example, if someone in California accesses a server located in Europe, the longer distance and complex routing lead to noticeable delays compared to accessing a server within the United States.
Network congestion is another common issue, especially during peak usage times. When too much data tries to pass through the same network segment at once, bottlenecks occur, slowing down data transmission. Areas with limited bandwidth feel this impact more acutely.
Routing inefficiencies can also add to the delay. Sometimes, data packets take unnecessarily long or indirect paths to their destination, bouncing through multiple network "hops." On top of that, hardware limitations in routers and switches can further slow things down, especially if the equipment isn’t up to modern standards.
Protocol overhead plays a role too. The time it takes for protocols like TCP/IP to establish connections can add up, particularly for websites that require many small requests. While newer protocols like HTTP/2 and QUIC aim to streamline this process, many websites still rely on older, less efficient protocols, which increases latency.
Server and Application Issues
Problems on the server side can significantly impact latency. A sluggish backend often results in higher Time to First Byte (TTFB), which is the time it takes for a server to respond to a request. This can be caused by unoptimized server code, database inefficiencies, or outdated server configurations.
Database bottlenecks are a frequent issue. When databases rely on poorly written queries or lack proper indexing, retrieving data becomes a slow process. Queries that process data sequentially instead of in parallel can add seconds to page load times, especially as the database grows in size.
Server overload happens when traffic spikes beyond what the server can handle. During these periods, response times slow down for everyone. Outdated hardware only makes the situation worse, as it struggles to keep up with modern demands.
An unoptimized application architecture can also drag performance down. Applications that rely on excessive database calls, use blocking operations, or implement inefficient algorithms will create latency problems, regardless of how powerful the hardware might be.
Client-Side Problems
Latency isn’t just about the network or server - problems on the user’s end can also slow things down. For instance, large assets like uncompressed videos, high-resolution images, and bloated JavaScript files take longer to download and process. These "payloads" are a key factor in website performance metrics.
Render-blocking resources are another headache. When a website relies on large CSS or JavaScript files that must load before the page can render, the user waits longer. This is especially noticeable on mobile devices, which often have limited bandwidth and processing power.
Device limitations can amplify latency issues. Older smartphones or computers with outdated browsers, limited memory, or slower processors struggle to handle modern websites. Mobile users are particularly vulnerable, as cellular networks generally have higher latency and lower bandwidth than wired connections.
Browser behavior also plays a role. How a browser caches resources, handles multiple connections, and prioritizes elements affects the overall experience. Modern browsers use techniques like prefetching and caching to speed things up, but poorly optimized websites fail to take full advantage of these features.
Metrics like Core Web Vitals - which include Largest Contentful Paint (LCP), Total Blocking Time (TBT), Interaction to Next Paint (INP), and Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS) - highlight client-side performance issues. When these metrics are poor, users experience slow load times and unresponsive interfaces, even if the network and server are functioning well.
sbb-itb-641714f
How to Reduce Latency and Improve Website Speed
Now that we’ve covered what causes latency, let’s shift gears to practical solutions. Tackling latency requires a mix of technical fixes and consistent monitoring. Many of these adjustments can lead to noticeable improvements in your website’s performance.
Technical Methods to Reduce Latency
One of the most effective ways to cut down on latency is by using Content Delivery Networks (CDNs). CDNs work by storing copies of your website on servers spread across different geographic locations. When someone visits your site, the CDN delivers content from the server closest to them. This reduces the distance data has to travel, speeding things up significantly.
Here’s an example: A user in California accessing a server located on the East Coast might face 80ms of latency. But if a CDN serves the content from a West Coast server, that latency could drop to just 20ms. For U.S.-based websites, it’s essential to ensure your CDN has strong coverage across key regions - like the East Coast, West Coast, Midwest, and South - to maintain consistent performance nationwide.
Caching is another powerful tool that works hand-in-hand with CDNs. With browser caching, static files like images, CSS, and JavaScript are stored directly on users’ devices, so they don’t need to be re-downloaded on subsequent visits. Meanwhile, server-side caching speeds up page generation by storing frequently requested data in memory instead of pulling it from a database every time.
Large, uncompressed images are notorious for slowing down websites, and image optimization offers a solution. Compressing images without sacrificing quality, resizing them for different devices, and using formats like WebP can significantly reduce load times. These steps are especially valuable for mobile users, where bandwidth can be limited.
Lazy loading is another game-changer. Instead of loading every image on a page right away, this technique delays loading non-essential images until users scroll down to them. This approach reduces initial page load times and saves bandwidth, making it particularly useful for image-heavy sites.
For developers, code optimization is key. Simplifying scripts, removing unnecessary plugins, and cutting down on HTTP requests can all speed up your site. Upgrading to modern protocols like HTTP/2 or HTTP/3 allows multiple requests to be processed simultaneously, further improving load times.
Finally, server-level improvements focus on backend efficiency. This includes optimizing database queries to cut processing times from 500ms to under 100ms, upgrading to faster server hardware, and ensuring your hosting setup can handle traffic spikes without slowing down. Together, these strategies create a smoother and faster user experience.
Using dCLUNK™ by CLUNKY.ai for Performance Analysis
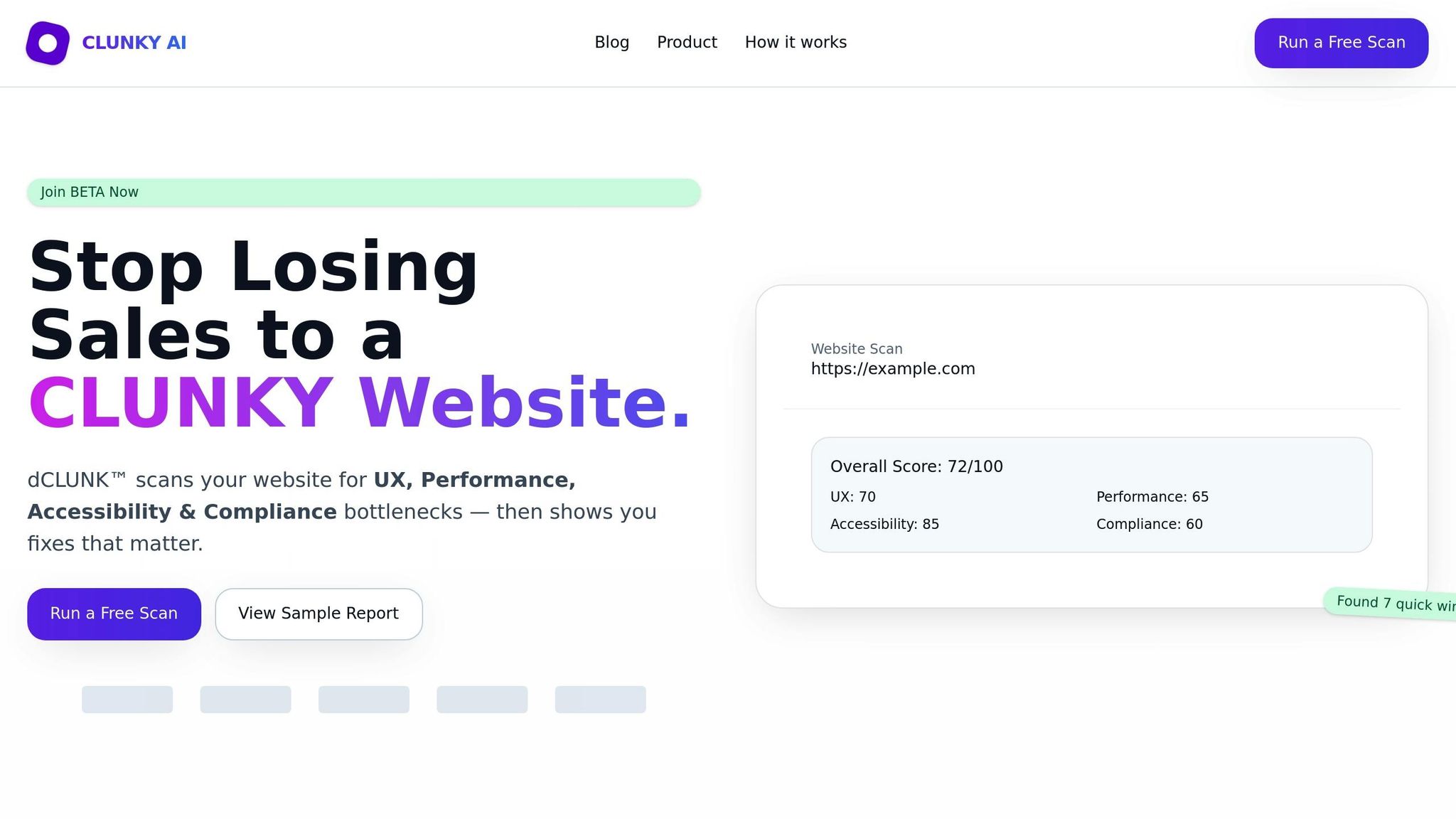
While implementing technical fixes is crucial, knowing where to start can save time and effort. That’s where dCLUNK™ by CLUNKY.ai comes in. This tool scans your entire website to pinpoint latency issues and performance bottlenecks.
The process is simple: enter your website URL, and within two minutes, dCLUNK™ provides a detailed analysis. It measures critical performance metrics like Time to First Byte (TTFB), Largest Contentful Paint (LCP), Total Blocking Time (TBT), Interaction to Next Paint (INP), and Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS). These metrics, part of Google’s Core Web Vitals, offer a clear view of how latency impacts user experience.
What makes dCLUNK™ stand out is its actionable approach. Instead of just identifying problems, it suggests prioritized fixes with estimated ROI. For example, it might flag a large image slowing down your homepage and recommend specific compression techniques or format changes to address the issue.
The tool uses read-only scans, much like how search engines crawl websites. This means it won’t disrupt your live site or affect users during the analysis. Once the scan is complete, you’ll receive an instant report that highlights issues by priority, allowing you to focus on the most impactful fixes first.
Here’s a real-world success story: Marco L., Product Manager at CraftMart, shared his experience:
"CLUNKY AI's audit exposed slow pages that scared off shoppers. Cleaning them up with the team gave us a 32% lift in completed checkouts."
This example underscores how reducing latency can directly benefit your business. A 32% increase in checkout completions demonstrates that faster websites don’t just improve metrics - they drive real results.
dCLUNK™ also supports ongoing maintenance. As you add new content, features, or plugins, website performance can degrade over time. Regular scans help you catch latency issues early, ensuring they don’t negatively affect user experience. The tool’s automated nature makes it easy to integrate performance checks into your routine.
Best of all, dCLUNK™ offers free scans, making it accessible to businesses of all sizes. You can even view sample reports to get a sense of what might be slowing down your site before diving into deeper analysis.
Monitoring and Measuring Latency for Ongoing Improvement
Improving latency isn’t a one-and-done task - it’s an ongoing process. Changes to your website or sudden traffic surges can bring latency issues back, potentially harming user experience. That’s why continuous monitoring is critical to maintaining strong performance.
Best Practices for Latency Monitoring
The most effective way to monitor latency combines Real User Monitoring (RUM) with synthetic testing. RUM collects data from actual visitors as they interact with your site, offering insights into how latency differs across devices, locations, and network conditions. On the other hand, synthetic testing simulates user visits in controlled environments, giving you consistent baseline measurements. Together, these methods can help you identify and address issues before they impact real users.
For most scenarios, daily or weekly monitoring strikes a good balance between simplicity and actionable insights. However, during critical moments like major updates, product launches, or marketing campaigns, real-time monitoring becomes essential. Automated alerts can be set up to notify your team when key thresholds are crossed - such as a Time to First Byte (TTFB) exceeding 200ms - allowing for quick action.
Key metrics to track include:
- TTFB: Measures how quickly your server responds to a request.
- Round-Trip Time (RTT): Tracks the time it takes for data to travel between the client and server.
- Page Load Time: Indicates how long it takes for the full page to load.
- Time to Render: Shows when a page becomes visually interactive.
Testing from multiple locations is also important, as it can uncover regional differences in performance. These insights help you pinpoint whether latency issues originate from the network, server, or client side.
Comparing Performance Against Standards
Once you’ve gathered monitoring data, you can benchmark your performance against industry standards. For instance, Google’s Core Web Vitals suggest keeping TTFB under 200ms and total page load times under 2 seconds for an optimal user experience. The stakes are high: 53% of mobile users will abandon a site if it takes more than 3 seconds to load, and even a 1-second delay in page response can reduce conversions by 7%.
For more detailed comparisons, tools like dCLUNK™ by CLUNKY.ai provide performance scores for metrics such as Largest Contentful Paint (LCP), Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS), and Interaction to Next Paint (INP). For example, if your site scores a 65, you can benchmark it against top-performing sites with scores in the 90s.
Regularly reviewing benchmarks helps you spot gradual performance declines or sudden setbacks. Automated alerts for dips in performance ensure you can respond quickly.
It’s also important to align benchmarks with your business goals. For instance, an e-commerce site might focus on optimizing checkout speed, while a news site might prioritize fast article load times. Tools like dCLUNK™ can help you identify which areas of improvement will deliver the most impact for your specific needs. When paired with the technical strategies covered earlier, consistent monitoring and realistic benchmarks can lead to sustained speed improvements for your website.
Key Points About Latency and Website Speed
Latency plays a major role in website performance, and even small delays can have a big impact on conversions. Research shows that a mere 100-millisecond delay in page load time can lower conversion rates by 7%. On mobile, the stakes are even higher - 53% of users will leave a site if it takes more than three seconds to load. Beyond frustrating users, slow-loading websites often rank lower on search engines, as Google's algorithms consider page speed when determining rankings. This creates a ripple effect: poor speed not only hurts conversions but also reduces organic traffic.
To optimize effectively, it's important to differentiate between latency and bandwidth. For instance, increasing bandwidth from 1 Mbps to 3 Mbps can significantly improve performance, but going from 3 Mbps to 5 Mbps offers only minor benefits, and moving from 5 Mbps to 10 Mbps barely makes a difference. On the other hand, reducing latency consistently improves performance, no matter the bandwidth level.
Latency can stem from various factors, including network hops, server load, and client-side limitations. This is why solutions like content delivery networks (CDNs), code optimization, and tools like dCLUNK™ are so valuable. These strategies address latency at its core, ensuring smoother performance.
The frustration caused by slow websites is real. On average, people estimate they spend about 9 minutes a day waiting for sluggish websites, which amounts to roughly two full days each year. This dissatisfaction often leads to abandoned transactions and damages customer loyalty.
Managing latency requires ongoing effort. Website updates, sudden traffic spikes, or infrastructure changes can reintroduce performance problems. Tools like dCLUNK™ from CLUNKY.ai help by identifying bottlenecks, offering prioritized fixes, and even estimating the ROI of those improvements. This proactive approach ensures that latency issues are addressed before they hurt user experience or business outcomes.
Reducing latency involves a combination of technical solutions - such as CDNs, optimized code, and strategic server placement - paired with regular monitoring and benchmarking. This investment pays off through better conversion rates, higher search rankings, and happier customers.
FAQs
How does latency affect mobile users differently than desktop users?
Mobile users often feel the effects of latency more than desktop users, and there are good reasons for this. Unlike desktops, which typically use faster wired or Wi-Fi connections, mobile devices often depend on cellular networks. These networks usually come with higher latency, which can slow down page loading and make browsing less responsive.
On top of that, mobile devices generally have less processing power and memory compared to desktops. This makes them more vulnerable to performance issues caused by delays. To give mobile users a smoother experience, focus on steps like optimizing images, enabling caching, and reducing server requests. Tools such as dCLUNK™ from CLUNKY.ai can pinpoint and fix these problems, helping to create a faster and more seamless browsing experience.
How can businesses measure and monitor website latency effectively?
Keeping an eye on your website’s latency is crucial for maintaining top-notch performance and delivering a seamless user experience. Start by leveraging tools that check your site’s response times across various locations and devices. These tools can pinpoint where delays are occurring and highlight areas that need attention.
For a deeper dive, you might want to try a website scanning tool like dCLUNK™ from CLUNKY.ai. It assesses your site’s performance, accessibility, and user experience, offering practical recommendations to tackle latency issues and enhance functionality. Regularly reviewing these metrics helps you quickly resolve problems and keep your website running smoothly.
What’s the difference between latency and bandwidth, and why does it matter for website speed?
When it comes to website performance, latency and bandwidth play crucial roles, but they address different aspects of the process. Latency is all about timing - it’s the delay between a user's request and the server's response. On the other hand, bandwidth measures how much data can flow through a connection within a specific time frame.
Here’s why this distinction matters: even with a high-bandwidth connection, excessive latency can still slow down page loading, frustrating users. To tackle latency, you can take steps like optimizing server response times, implementing a Content Delivery Network (CDN), or enabling caching. These strategies can make a noticeable difference in website speed and user experience.
Related Posts
Tags AccessibilityPerformanceUser Experience
Category Website Optimization